In addition to the processing or manufacturing zone, sub-projects for transport, utilities, power, environment, urban land and real estate development form an integral part of an integrated industrial area. These facilities are non-core activities for SIDCs, hence inefficiency is inherent in such projects. Infrastructure projects related to transport, utilities like power, energy, water supply (including for industrial purposes), waste water treatment, collection and treatment, site restoration, social infrastructure, housing development and tourism (especially business tourism) are some of the prime sectors that can be targeted for development / investments on PPP basis. The assessment criteria for investment in above sectors on PPP basis are briefly discussed in this note.
—————————————————————————
A state industrial development corporation (SIDC) prima-facie focuses on provision of infrastructure to the processing / manufacturing zones or industries. Traditionally, SIDCs have been acquiring land, undertaking physical planning, developing plots for allocation and providing infrastructure (road, street lights, electricity, water supply, waste water disposal lines etc.). These activities are generally undertaken in-house or on EPC basis. The costs are recovered by selling the plots to the industries and charging lump-sum up front cost for providing infrastructure. Further, the costs for O&M of water supply and electricity are recovered on actual consumption basis.
An SIDC invests certain resources in building infrastructure and then recovers the same through allotment (sale) of plots to industries. Certain facilities having recurring costs are charged on periodic basis to the industries using them (water, electricity, etc.) where as certain facilities (road street, lights, etc) are refurbished or repaired on need basis by the SIDC. For such instances, the SIDC may ask for contribution from the Industries Association (if any) or source funds from any government scheme / grant and/or maintain its own funds generated by phased sale of plots or resale of plots (transfer fees).
In most of the cases, O&M of such areas suffer due to lack of funds available on the part of SIDC. SIDC also has to continuously maintain a balance in terms of developing / promoting new industrial area projects as well as improving / providing funds for older industrial areas. As the gestation period for an industrial area in India is very long, sometimes extending to a decade or so, most SIDCs end up being constrained in terms of funds and resources.
Further, in case of an integrated industrial area, in addition to the processing / manufacturing zone, it is expected to comprise of sub-projects for transport, utilities, power, environment, urban land and real estate development. Hence, SIDCs have to cater to non-processing facilities in addition to their regular expertise. These facilities are non-core activities for SIDCs, hence inefficiency is inherent in such projects, if undertaken by SIDCs on its own. With these facilities becoming increasingly important in determination of competency of an integrated industrial area, SIDCs across India are increasingly looking forward to utilising the private sector expertise, experience and efficiencies in such projects.
Infrastructure projects related to transport, utilities like power, energy, water supply (including for industrial purposes), waste water treatment, collection and treatment, site restoration, social infrastructure, housing development and tourism (especially business tourism) are some of the prime sectors that can be targeted for development / investments on PPP basis.
The following table provides an indicative and non-exhaustive list of projects (infrastructure and utilities) that may be part of an Integrated Industrial Area
|
Project / Sector | Importance of Project to success of Integrated Industrial Area |
Project Priority for early development |
|
Regional Road Connectivity to Integrated Industrial Area |
Improved connectivity with rest of the region is a precursor to attract investment in the region | High significance in early stages of development as improved accessibility is an incentive to industries and EXIM traffic |
| Regional Rail Connectivity to Integrated Industrial Area | Improved connectivity with rest of the region is a precursor to attract investment in the region |
High significance in early stages of development as improved freight connectivity is an incentive to industries and EXIM traffic |
|
Logistic Park | World Class Logistics Services is a necessity to promote the integrated industrial area efficiency and attractiveness to investment | High significance in early stages of development as improved freight logistics is an incentive to industries and EXIM traffic |
|
Water Source Augmentation | Precursor to setting up the Integrated Industrial Region |
High significance in early stages of development |
|
Water Transmission | Precursor to setting up the Integrated Industrial Region |
High significance in early stages of development |
|
Water Distribution | Precursor to setting up the Integrated Industrial Region |
High significance in early stages of development |
| Collection of Waste Water | Precursor to setting up the Integrated Industrial Region |
High significance in early stages of development |
|
Treatment of Waste Water | Precursor to setting up the Integrated Industrial Region | High significance in early stages of development |
|
Recycling / Disposal of Treated Waste Water | Precursor to setting up the Integrated Industrial Region | High significance especially in later stages of development as water is a scarcity |
|
Power Plants |
Precursor to setting up the Integrated Industrial Region |
Moderate significance in case of large industries (captive power plants) |
|
Renewable Energy Plants |
Alternative source of energy |
Low |
| Power Transmission | Precursor to setting up the Integrated Industrial Region |
High significance in early stages of development |
|
Power Distribution |
Precursor to setting up the Integrated Industrial Region |
High significance in early stages of development |
|
Self Contained Knowledge Park / other social infrastructure |
Provision of Industrial / vocational training, other universities, colleges, medical institutes and schools for developing the industrial knowledge base |
Considerable significance through out |
|
Arterial Roads & Urban Expressways | Quality connectivity within the area is a precursor to attract investment in the region |
High significance in early stages of development as improved accessibility is an incentive to residents / employees |
|
Mass Transit | Quality connectivity within the area is a precursor to attract investment in the region |
Limited significance in early stages of development |
|
Housing & Commercial | Provision of housing & commercial facilities is crucial to attract human resources to reside in areas close to the industrial zones |
High significance in all stages of development so as to release pressure from mass transport system |
|
Low Cost Housing | Provision of affordable housing is crucial to attract labour force to reside in areas close to the industrial zones | High significance in all stages of development so as to attract labour force and release pressure from mass transport system |
|
Tourism / Recreational Infrastructure |
Potential for large scale real estate development |
High significance in all stages to make tourism a contributing industry |
|
Solid Waste Management | Provision of a clean and hygienic environment |
Limited significance in early stages of development |
Assessment Criteria for Investment on PPP basis
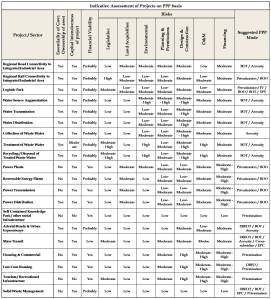
For ensuring success in terms of attracting PPP investments for various projects in the sectors as mentioned above, it would be necessary to assess the projects for various risks with due consideration to following factors:
Project need & key performance targets
Relevance of projects to achieving the overall project goals, contribution to the success of the Integrated Industrial Area, priority of the project in terms of the early development of the Integrated Industrial Area and manageability of the project within the timescale and budget of the government agency
Funding and ownership assumptions
For ensuring a project’s suitability for development on PPP basis, it would be important to determine the scale of investment and operational costs, and importance of assets to remain with the Government. Typically, a regional-scale infrastructure development project needs large capital for addressing construction costs, life cycle and maintenance costs and costs of the associated risks.
In terms of ownership, infrastructure is considered to have strong public good characteristics and also form a part of strategic national/state assets. In some PPP models, the government can either hand-over the assets at the end of the concession period sharing twin benefits of government oversight and private sector efficiency or forward the assets to the private party.
Risk Assessment
Generally, PPP projects transfer certain risks to the private sector and provide incentives for the assets to be properly maintained. Among the risks that can be assumed by the private partner are:
- Legislative and policy changes
- Land acquisition
- Environmental constraints
- Risks associated with the physical damage to the assets
- Design and construction risk covering the required standards of delivery, excessive cost overruns during the construction, completing the facility on time and technological risks
- Operation and maintenance risk covering the underlying costs to the service delivery operator and future costs associated with the asset
The following table provides for indicative assessment and risk exposure of the above mentioned projects. It is to be noted that the importance and level of risk is likely to vary should be thoroughly evaluated on case to case basis.